TYPES OF COMMUNICATION
The
word communication has been derived from the Latin word 'Communis' which means 'common'. Thus, communication means sharing
of ideas in common. "When we
communication," says Wibur
Schramn, "We are trying to establish a 'commonness' with someone. That
is we are trying to share information, an idea or an attitude. The essence of
communication is getting the receiver and the sender 'turned' together for a
particular massage."
Louis A, Allen defines communication as,
"communication is the sum of all the things one person does when he wants
to create understanding in the mind of another. It is a bridge of meaning. It
involves a systematic and continuous process of telling, listening and
understanding."
Koontz and O'Donnell are of the opinion
"communication is a way that one organization member shares meaning and
understanding with another."
Characteristics: Nature of
Communication
1.
It involves at Least Two Persons
2.
Message
is a Must.
3.
Communication
May be Written Oral or Gestural:
4.
Communication
is Two Way Process:
5.
Its
Primary Purpose is to Motivate a Response
6.
Communication
May be Formal or Informal
7.
It
Flows Up and Down and Side to Side:
8.
It
is an Integral Part or the Processor Exchange:
Methods (Channels) or Types of Communication:
Communication
may be classified into several categories on the following basis:
1. On
the Basis of Organizational Structure or Relationship:
a.
Formal
Communication
b.
Informal
Communication or Grapevine.
2. On
the Basis of Flow or Direction:
a.
Downward
Communication
b.
Upward
Communication
c.
Horizontal
or Lateral or Sideward Communication
d.
Diagonal
Communication.
3. On
the Basis of Methods or Media used or Expression:
a.
Written
Communication
b.
Oral
Communication
c.
Gestural
or Non-Verbal Communication.
A)
On
the Basis of Relationship or Organization Structure:
I)
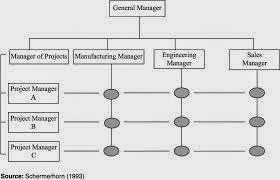
Formal Communication: Formal communication is that
which takes place through the formal channel of the organization structure
deliberately and consciously established by the management. It implies the flow
of the information along the lines of authority formally established in the
enterprise. Members of the enterprise are expected to communicate with one
another strictly as per channels laid down in the structure. Such
communications are generally in writing and may take any of the following
forms:
1.
Policy
Manuals;
2.
Procedural
and Rule Books;
3.
Memoranda
Papers and Orders;
4.
Official
Meeting;
5.
Interviews,
etc.
II)
Informal Communication or
Grapevine:
Communication arising out of all those channels of communication that fall
outside the formal channel is known as informal communication or the grapevine.
It is built around the social relationship of members of the organization.
Informal communication does not follow lines of authority as is the case of
formal communication. It arises due to the personal needs of the members of an
organization and exists in every organization. Such communication is usually
oral and exists in even by simple glance ,gesture, smile or silence.
B)
On
the Basis of Flow or Direction:
I)
Downward
Communication: Communication
between a superior and subordinate is known as vertical communication. Vertical
communication may be downward vertical communication or upward vertical
communication. Downward communication means communication which flows from a
superior to a subordinate.
The important examples of downward communication
are:
1)
Notices
2)
Circulars
3)
Instructions
4)
Orders
5)
Letters
6)
Memos
II) Upward Communication: Upward
communication means the flow of information from the lower levels of the
organization to the higher levels of authority .It passes from subordinate to
superior as that from worker to foreman, from foreman to manager, from manager
to general manager and form general manager to the chief executive or the board
of directors. It includes opinions, ideas, suggestions, complaints, grievances,
appeals, reports, etc.
Upward
Communication is Needed:
1)
To
create receptiveness of communication
2)
To
create a sense of belongingness through active participation
3)
To
evaluate the effectiveness of communication
4)
To
increase morale of employees
5)
To
make improvements in managerial decisions
6)
To
co-ordinate efforts; and
7)
To
know ideas of each individual in the organization.
III) Horizontal, Lateral or Sideward
Communication: The transmission of information and understanding
between people on the same level of organization hierarchy is called the horizontal
communication. This type of communication is also known as lateral or sideward
or crosswise communication. Usually, it pertains to inter-departmental
communication, i.e., the communication between two departmental managers
working at the same level of organization or among subordinates working under
one boss.
IV) Diagonal Communication: The transfer of information
between people who are neither in the same department nor on the same level of
organization hierarchy is called diagonal communication. For example, when the
assistant marketing manager communicates with the accounts clerk directly, it
is the case of diagonal communication. This type of communication increases the
organizational efficiency by speeding up information and cutting across
departmental barriers.
C)
On
the basis of media or expression:
The
various media of communication have been studied as under:
1)
Written
Communication;
2)
Oral
Communication;
3)
Gestural
or Non-verbal Communication.
1)
Written
Communication: communication
through words, may be in writing or oral. Written communication implies
transmission of message in back and white it includes diagrams, pictures,
graphs, etc. have to be transmitted in writing for efficient running of the
organization. written communication ensures that everyone concerned has the
same information. It may take the following forms:
1)
Reports
2)
Circulars
3)
Magazines
4)
Manuals
5)
Memoranda
6)
Newspapers
7)
Pictures,
diagrams, graphs, etc.
Merits or Advantages of Written
Communication:
1)
It
ensures transmission of information in uniform manner, i.e. every one concerned
has the same information.
2)
It
provides a permanent record of communication for future reference.
3)
It
is an ideal way of transmitting length messages.
Demerits or Disadvantages of
Written Communication:
1)
It
is expensive
2)
It
is time consumption
3)
It
becomes difficult to maintain secrecy about a written communication.
2) Oral Communication: Oral
or verbal communication implies the conveying of message through spoken words.
It is face to face communication between individuals and includes communication
through telephone, intercom and public speech, etc. in every organization, a
great deal of information is exchanges orally and it is generally preferred to
written communication.
Theo
Haimann pointed out, "the human voice can impart the message with 'meaning
and shading which even long pages of written words simply cannot convey."
It may take the following forms depending upon the
need and situation,
1)
Face
to face talks
2)
Telephonic
conversation
3)
Interviews
4)
Meetings
5)
Lectures
6)
Conferences.
3) Gestural or Non verbal
Communication: Communication does not mean merely written .or oral
messages. It includes everything that may be used to convey meaning from one
person to another, e.g., movement of lips or the wink of an eye or the wave of
hands may convey more meaning than written or oral words. Expression through
body parts is known as gestural or non-verbal communication. It includes facial
expression, movement of lips, wink of an eye, nodding of heads, movement of
hands, a sense of humour or a mere silence, etc.

Comments