KEY TERMS OF MANAGEMENT FROM DELEGATION TO MANAGERIAL GRID
1.
Delegation: The transfer of authority from a manager to a
subordinate.
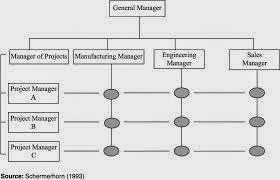
2.
Span
of management:
The number of employees reporting to a manager. Also known as span of control.
3.
Centralization: Decision authority is concentrated at the top
of the organizational hierarchy.
4.
Decentralization: Upper management pushes decision-making authority
to lower organizational levels.
5.
Tall structure: Characterized by a large number of
hierarchical levels and a relatively narrow span of management.
6.
Flat
structure:
Characterized by few hierarchical levels and a broad span of management.
7.
Organizational
change: The adoption
and implementation of innovations and new behaviors by an organization.
8.
Reactive change: Changes that occur after external forces have
affected organizational performance.
9.
Proactive change: Changes initiated in anticipation of future
events and opportunities.
10. Sequence of organizational
change
• Environmental and internal forces → Need
for change → Initiate change → Implement change
11.
Performance
gap: The gulf between desired and actual
performance.
12. Initiating
change :
-
Search:
Discovering developments internally and externally that can satisfy a
need for change.
-
Creativity: The creation of innovative solutions for
organizational problems.
-
Idea champion: An employee who determines a need exists
within an organization and actively strives to satisfy it.
-
New venture team: A temporary task force assigned to solving
organizational problems and developing innovations.
-
New venture fund: A fund established to provide resources for
individual and group-developed innovations.
13. Implementing change
-
Force field analysis: Determining which forces drive or resist
proposed changes.
-
Communication and education: Providing employees with detailed information
on impending organizational changes through presentations and info papers.
-
Participation:
Involves employees with the organizational change process.
-
Negotiation: A formal bargaining process between
management and subordinate business units and employees that serves to set
changes in terms that are mutually acceptable.
-
Coercion: The use of formal managerial power to force
changes upon an organization.
-
Top management support: The public expressions by executive
management in support of organizational changes.
14. Categories of organizational
change
-
Technology changes: A change that incorporates developing
technology that improves communication, management, and production.
-
Product changes: A significant change in a company’s product
or service.
-
Structural changes: Any adjustment of an organization’s
management or functional structure.
-
Cultural changes: A change in employee beliefs, values, and
norms.
15.
Leadership: An individual’s ability to influence a person
or group of people to perform functions that reach goals.
16.
Trait
theories: Theories
that promote individual personality traits as factors that determine leadership
effectiveness.
17.
Behavior
theories: Theories
that promote behaviors as factors in determining leadership effectiveness.
18. Ohio State Studies
-
Initiating structure: The
structuring by a manager of roles to best achieve goals.
-
Consideration: The propensity of a manager to form
professional relationships based on trust, respect, and regard for
subordinates’ feelings.
19. University
of Michigan Studies
-
Employee-oriented leader: A leader who promotes interpersonal
relationships.
-
Production-oriented leader: A leader who promotes task- orientation.
20.
The Managerial Grid: A matrix that graphically illustrates
leadership styles by identifying 81 different leadership styles.


Comments