Money Supply and its Determinants
Introduction
The supply of money is a stock at a particular point of time, though it conveys the idea of a flow over time. The term ‘the supply of money’ is synonymous with such terms as ‘money stock’, ‘stock of money’, ‘money supply’ and ‘quantity of money’.
The supply of money is a stock at a particular point of time, though it conveys the idea of a flow over time. The term ‘the supply of money’ is synonymous with such terms as ‘money stock’, ‘stock of money’, ‘money supply’ and ‘quantity of money’.
The supply of money at any moment is the total
amount of money in the economy. There are three alternative views
regarding the definition or measures of money supply.
·
The most common view is associated with the traditional
and Keynesian thinking which stresses the medium of exchange function
of money.
Forms of MS
M1 = C + DD (Demand Deposit)
M2= M1 +TD (Time
Deposit)
M3= M2 + Liabilities
of NBAFI
Determinant of MS
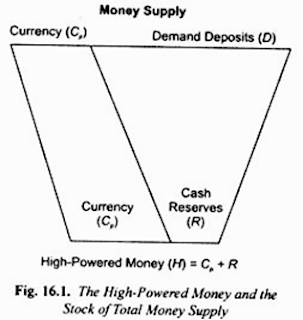
1. High powered Money (H= C + R), (M = C + D)
The H Theory of Money Supply’.
However, it is more popularly called ‘Money-multiplier Theory of Money Supply’
because it explains the determination of money supply as a certain multiple of
the high- powered money (M =m * H)
2. Money Multiplier:
·
Money
multiplier is the degree to which money
supply is expanded as a result of
the increase in high-powered money. Thus
·
m = M/H Rearranging
we have, M = H.m
·
Change in
the high-powered money is decided and controlled by central Bank, the money
multiplier determines the extent to which decision by central Bank regarding
the change in high-powered money will bring about change in the total money supply in the economy
·
m= Cr + 1
/Cr +rr(t +1)
From above it follows that money supply in
the economy is determined by the following:
o
H, that
is, the amount of high-powered money,
which is also called reserve money
o
r, that
is, cash reserve ratio of banks (i.
e., ratio of currency reserves to deposits of the banks)
o
This cash
reserve ratio of banks determines the magnitude of deposit multiplier.
o
k, that
is, currency-deposit ratio of the public.
3. Cash Reserve Ratio of the Banks and the
Deposit Multiplier (CRR)
Because of fractional
reserve system, with a small increase in cash reserves with the banks, they are
able to create a multiple increase in total demand deposits which are an
important part of money supply. The ratio of change in total deposits to a
change in reserves is called the deposit multiplier which depends on cash
reserve ratio (CRR increase MS decrease)
4. Currency-Deposit Ratio of the Public and Money Multiplier (Cr)
When as a result of
increase in cash reserves, banks start increasing demand deposits, the people
may also like to have some more currency with them as money balances. This
means during the process of creation of demand deposits by banks, some currency
is leaked out from the banks to the people.
Conclusion
·
Theory of
determination of money supply explains how a given supply of high-powered money
(which is also called monetary base or reserve money) leads to multiple
expansion in money supply through the working of money multiplier. We have seen
above how a small increase in reserves of currency with the banks leads to a
multiple expansion in demand deposits by the banks through the process of
deposit multiplier and thus causes growth of money supply in the economy.
·
The money
multiplier can be defined as increase in money supply for every rupee increase
in cash reserves (or high-powered money), drainage of currency having been
taken into account. Therefore, money multiplier is less than the deposit
multiplier.
·
It is
worth noting that rapid growth in money supply in India has been due to the
increase in high-powered money H, or what is also called Reserve Money (Lastly
Reserve Bank of India, the money multiplier remaining almost constant.
·
The money
supply in a country can be changed by Central Bank by undertaking open
market operations, changing minimum required currency reserve-deposit ratio,
and by varying the bank rate. The main source of growth in money supply in
India is creation of credit by central Bank for Government for financing its budget
deficit and thus creating high-powered money.
·
Further,
though the required currency reserve-deposit ratio of banks can be easily
varied by CB, the actual currency reserve-deposit ratio cannot be so easily
varied as reserves maintained by banks not only depend on minimum required cash
reserve ratio but also on their willingness to hold excess reserves.
·
Lastly, an
important noteworthy point is that though money multiplier does not show much
variation in the long run, it can change significantly in the short run causing
large variations in money supply. This unpredictable variation in money
multiplier in the short run affecting money supply in the economy prevents the
Central Bank of a country from controlling exactly and precisely the money
supply in the economy.

Comments