MACROECONOMIC UPDATE 1 : MONEY SUPPLY (APRIL 2020)
Money plays an important role in an economy and is a key component of the transmission mechanism from monetary policy to economic activity and inflation. Conceptually, the notion of money has been linked to the formulation of monetary policy and the need for money growth to be in line with the desired real growth rate and level of inflation, given an assumption on the velocity of money. Monetary growth can also impact on asset prices in an economy. Money aggregates measure the money available to money-holding sectors in the economy for making purchases of goods, services, nonfinancial assets and financial assets, and are closely monitored by the central bank when determining decisions that affect the short-term policy interest rate and/or the level of the monetary base.
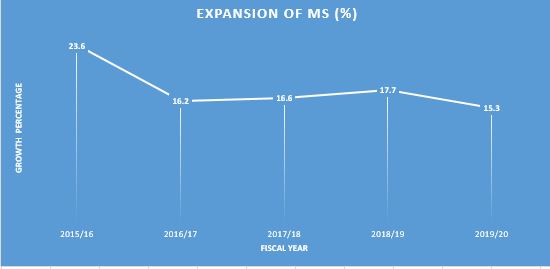
The value for broad money (M2) growth (annual %) in Nepal was 15.30% as of 2019/20. As the graph below shows, over the past five years this indicator reached a maximum value of 23.6 in fiscal year 2015/16 and a minimum value of 15.30% in this year fiscal year 2019/20. M2 registered at Rs 3901018.7 million, on y-o-y basis, M2 expanded by 15.3 percent in fiscal year 2020. This expansion is lower as compared to previous year FY 2018/19 as it was expanded by 17.7% (yoy).As shown in following table 1(fiscal year 2018/19), the monetary aggregates reached at Rs. 249165.2 million, Rs 1278671.2 million and Rs. 1427813.6 million as of demand deposit, saving/call deposit and time deposits respectively which was quite stable as in the corresponding period of the previous year.
Therefore ,broad money is at the heart of the monetary transmission mechanism and consequently plays an important role in the assessment of inflationary pressures.
Source: Nepal Rastra Bank, Current
Macroeconomic and Financial Situation (various year)
Figure 1: Growth Rate of M2
.


Comments