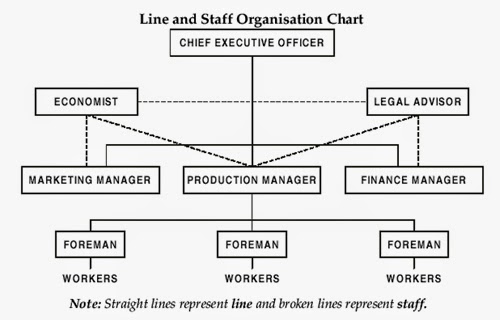
COMPARISON BETWEEN SCIENTIFIC AND ADMINISTRATIVE MANAGEMENT THEORY
Firstly, the scientific management approach is based on the concept of planning of work to achieve efficiency, standardization, specialization and simplification. The approach to increased productivity is through mutual trust between management and workers. Taylor (1947) proposed four principles of scientific management: a) Science, not rule-of-thumb; b) Scientific selection of the worker; c) Management and labor cooperation rather than conflict; and scientific training of workers. The concept of scientific management was developed by Frederick Taylor (1856-1915) in late 19th century. The core idea of scientific management was to increase the efficiency of workers through rationalization and standardization of work. The main concepts and techniques used to achieve increased efficiency were division of labour, time and motion studies, work measurements and piece-...